Website speed optimization is no longer optional—it’s essential for success in 2025. In fact, a one-second delay in page load time can reduce conversions by 7%. Moreover, Google uses page speed as a ranking factor, making optimization critical for SEO performance.
This comprehensive guide covers 25+ proven website speed optimization techniques. Additionally, you’ll learn how to improve Core Web Vitals, optimize images, implement caching, and achieve lightning-fast load times. As a result, you’ll deliver superior user experiences and improve search rankings.
- Why Website Speed Optimization Matters
- Understanding Core Web Vitals
- Measuring Website Speed
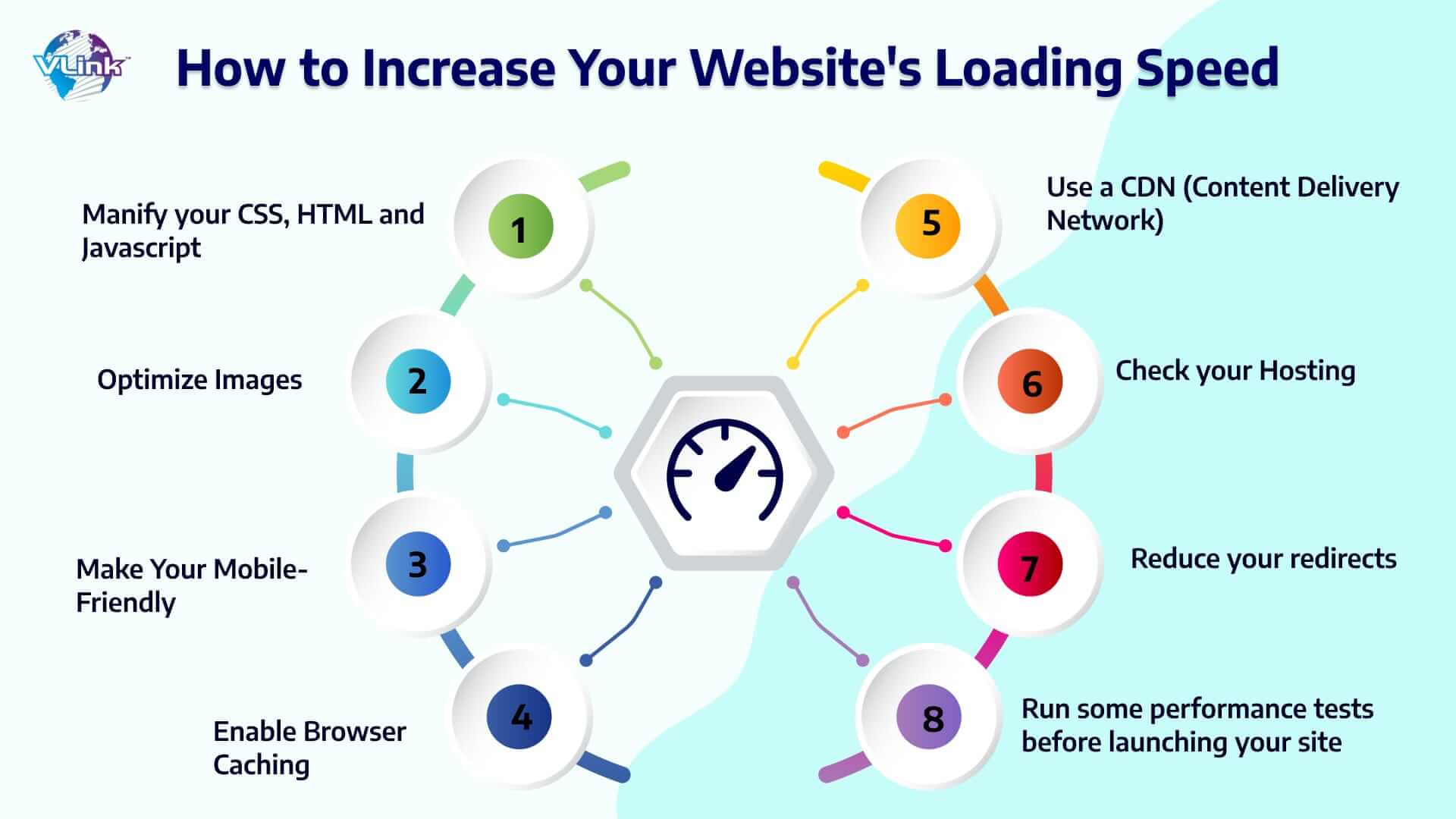
- Image Optimization Techniques
- Caching Strategies
- Minification and Compression
- JavaScript Optimization
- CSS Optimization
- Database Optimization
- Server and Hosting Optimization
- WordPress-Specific Optimization
- Mobile Optimization
- Advanced Optimization Techniques
- Monitoring and Maintenance
- Common Speed Optimization Mistakes
- Website Speed Optimization Checklist
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
Why Website Speed Optimization Matters
1. User Experience and Engagement
Fast websites keep visitors engaged. Specifically, your LCP should be less than 2.5 seconds to provide a good user experience. Moreover, users abandon slow-loading sites within seconds. Therefore, speed directly impacts bounce rates and conversions.
2. SEO and Search Rankings
Google uses Core Web Vitals as ranking factors in search results. Additionally, faster sites rank higher than slower competitors. Therefore, website speed optimization improves organic visibility and traffic.
3. Conversion Rates and Revenue
Websites that load within 2 seconds have higher engagement rates, lower bounce rates, and increased conversions. Furthermore, every millisecond counts—speed optimization directly increases revenue.
4. Mobile Performance
Over 60% of traffic comes from mobile devices. Moreover, Google uses mobile-first indexing for rankings. Therefore, mobile speed optimization is crucial for success.
5. Competitive Advantage
Fast websites outperform slow competitors. Additionally, speed creates positive first impressions. Therefore, optimization provides measurable business advantages.
Understanding Core Web Vitals
Google’s Core Web Vitals measure real-world user experience. Specifically, Core Web Vitals measure user experience in loading, interactivity, and visual stability. These three metrics are:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
LCP measures how quickly the main content loads. Specifically, if your LCP is under 2.5 seconds, it’s considered “Good”. Additionally, LCP between 2.5-4 seconds needs improvement. Finally, over 4 seconds is poor.
How to Optimize LCP:
- First, optimize images and use modern formats
- Additionally, implement server-side rendering
- Moreover, preload critical resources
- Furthermore, upgrade hosting infrastructure
- Finally, minimize render-blocking resources
Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
INP measures how quickly pages respond to interactions. Specifically, if your INP is under 200 milliseconds, it’s considered “Good”. Moreover, INP between 200-500ms needs improvement. Finally, over 500ms is poor.
How to Optimize INP:
- First, minimize JavaScript execution time
- Additionally, break up long tasks
- Moreover, optimize event handlers
- Furthermore, defer non-critical scripts
- Finally, reduce DOM size
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
CLS measures visual stability during loading. Specifically, scores under 0.1 are good. Additionally, 0.1-0.25 needs improvement. Finally, over 0.25 is poor.
How to Optimize CLS:
- First, include size attributes for images
- Additionally, reserve space for ads and embeds
- Moreover, avoid inserting content above existing content
- Furthermore, use transform animations instead of position changes
- Finally, preload web fonts
Measuring Website Speed
Essential Testing Tools
Use these tools to measure performance:
Google PageSpeed Insights PageSpeed Insights provides comprehensive performance analysis. Additionally, it shows both lab and field data. Moreover, it includes specific optimization recommendations.
GTmetrix GTmetrix combines multiple performance metrics. Furthermore, it provides detailed waterfall charts. Finally, it tracks performance over time.
WebPageTest WebPageTest offers advanced testing options. Moreover, it simulates different devices and connections. Additionally, it provides filmstrip views of loading.
Chrome DevTools Chrome’s built-in Lighthouse tool measures Core Web Vitals. Additionally, it identifies performance issues. Moreover, it provides actionable recommendations.
Google Search Console Search Console shows real user data. Furthermore, it identifies pages needing improvement. Finally, it tracks Core Web Vitals over time.
Image Optimization Techniques
Images typically account for 50% of page weight. Therefore, image optimization is critical for speed.
1. Choose the Right Format
Modern image formats reduce file sizes significantly:
WebP Format: WebP offers high compression rates similar to JPEG and PNG but with significantly smaller file sizes. Additionally, it supports transparency and animation.
AVIF Format: AVIF provides even better compression than WebP. Moreover, browser support continues growing. Therefore, AVIF is the recommended choice for 2025.
JPEG for Photos: Use JPEG for photographs and complex images. Additionally, adjust quality settings for optimal compression.
PNG for Graphics: Use PNG for graphics requiring transparency. Moreover, PNG maintains crisp lines and text.
2. Compress Images Effectively
Lossy Compression: Lossy compression reduces file sizes by permanently removing certain information and details from image files. Additionally, quality loss is often imperceptible. Therefore, lossy compression is ideal for web use.
Lossless Compression: Lossless compression maintains perfect quality. However, file size reduction is smaller. Therefore, use lossless for critical images only.
Compression Tools:
- TinyPNG – Smart lossy compression
- Squoosh – Advanced compression control
- ImageOptim – Mac batch compression
- ShortPixel – WordPress plugin
3. Implement Responsive Images
Serve appropriately sized images:
<img srcset="image-320w.jpg 320w,
image-640w.jpg 640w,
image-1024w.jpg 1024w"
sizes="(max-width: 320px) 280px,
(max-width: 640px) 600px,
1024px"
src="image-1024w.jpg"
alt="Descriptive text">
Additionally, this delivers optimal images for each device. Moreover, it reduces unnecessary data transfer.
4. Lazy Load Images
Lazy loading defers the loading of images until they enter the user’s viewport, reducing initial page load times. Moreover, implementation is simple:
<img src="image.jpg" loading="lazy" alt="Description">
Furthermore, lazy load below-the-fold images. However, never lazy load above-the-fold content.
5. Optimize Image Dimensions
Resize images to actual display size. Specifically, don’t rely on CSS to scale images. Moreover, use server-side resizing when possible. Therefore, serve exact dimensions needed.
6. Use Image CDN
Image CDNs optimize and deliver images globally. Additionally, they automatically convert formats. Moreover, they cache images worldwide. Therefore, CDNs dramatically improve image performance.
Caching Strategies
Caching stores frequently accessed data for faster retrieval.
Browser Caching
Set appropriate cache headers:
<IfModule mod_expires.c>
ExpiresActive On
ExpiresByType image/jpg "access plus 1 year"
ExpiresByType image/jpeg "access plus 1 year"
ExpiresByType image/gif "access plus 1 year"
ExpiresByType image/png "access plus 1 year"
ExpiresByType image/webp "access plus 1 year"
ExpiresByType text/css "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType application/javascript "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType text/html "access plus 600 seconds"
</IfModule>
Additionally, cache static resources for long periods. Moreover, version filenames when updating.
Server-Side Caching
Implement server caching layers:
Page Caching: Store complete HTML pages. Additionally, serve cached pages instantly. Moreover, regenerate periodically.
Object Caching: Cache database queries and results. Furthermore, use Redis or Memcached. Therefore, reduce database load.
Opcode Caching: Enable PHP opcode caching. Moreover, OPcache is built into modern PHP. Therefore, enable it for better performance.
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
CDNs deliver content from locations closest to users:
Popular CDN Providers:
- Cloudflare – Free tier available
- Amazon CloudFront – Global reach
- Fastly – Real-time purging
- BunnyCDN – Affordable pricing
Additionally, CDNs reduce server load. Moreover, they improve global performance. Therefore, CDNs are essential for optimization.
Minification and Compression
1. Minify CSS and JavaScript
Remove unnecessary characters from code:
Before Minification:
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}
After Minification:
body{margin:0;padding:0;font-family:Arial,sans-serif}
Minification Tools:
2. Enable Gzip Compression
Compress text-based resources:
<IfModule mod_deflate.c>
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/html
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/css
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/javascript
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/javascript
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/json
</IfModule>
Additionally, Gzip reduces file sizes by 70-90%. Moreover, all modern browsers support it. Therefore, always enable compression.
3. Use Brotli Compression
Brotli provides better compression than Gzip:
<IfModule mod_brotli.c>
AddOutputFilterByType BROTLI_COMPRESS text/html text/plain text/xml text/css
AddOutputFilterByType BROTLI_COMPRESS application/javascript application/json
</IfModule>
Furthermore, Brotli is supported by modern browsers. However, fallback to Gzip for older browsers.
JavaScript Optimization
1. Defer Non-Critical JavaScript
Load JavaScript after page content:
<script src="script.js" defer></script>
Additionally, use async for independent scripts:
<script src="analytics.js" async></script>
Moreover, defer prevents render blocking. Therefore, pages load faster.
2. Remove Unused JavaScript
Audit and remove unnecessary code:
Chrome DevTools Coverage: Identify unused code in DevTools Coverage tab. Additionally, remove or lazy load unused code. Moreover, split code into smaller bundles.
3. Code Splitting
Split JavaScript into smaller chunks:
// Dynamic import
button.addEventListener('click', async () => {
const module = await import('./heavy-feature.js');
module.initialize();
});
Furthermore, load code when needed. Therefore, reduce initial bundle size.
4. Optimize Third-Party Scripts
Third-party scripts often slow sites significantly:
- First, audit all third-party scripts
- Additionally, load scripts asynchronously
- Moreover, use lightweight alternatives
- Furthermore, implement lazy loading
- Finally, remove unnecessary scripts
Each third-party script slows a page down by 34 ms on average. Therefore, minimize third-party code.
CSS Optimization
1. Inline Critical CSS
Embed critical CSS directly in HTML:
<head>
<style>
/* Critical CSS here */
body { margin: 0; }
header { height: 60px; }
</style>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css" media="print" onload="this.media='all'">
</head>
Additionally, this prevents render blocking. Moreover, pages display faster.
2. Remove Unused CSS
Identify and remove unused styles:
Tools for Detection:
3. Optimize CSS Delivery
Load CSS efficiently:
<!-- Preload critical CSS -->
<link rel="preload" href="critical.css" as="style">
<!-- Load non-critical CSS asynchronously -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="non-critical.css" media="print" onload="this.media='all'">
Furthermore, this improves perceived performance significantly.
Database Optimization
1. Optimize Database Queries
Inefficient queries slow sites dramatically:
Best Practices:
- First, add indexes to frequently queried columns
- Additionally, avoid SELECT * queries
- Moreover, use LIMIT for large result sets
- Furthermore, cache query results
- Finally, use EXPLAIN to analyze queries
2. Clean Up Database
Regular maintenance improves performance:
- First, remove post revisions
- Additionally, delete spam comments
- Moreover, clean transient data
- Furthermore, optimize database tables
- Finally, remove unused plugins/themes
3. Use Database Caching
Implement object caching:
// WordPress example
$cached_data = wp_cache_get('my_key');
if (false === $cached_data) {
$cached_data = expensive_query();
wp_cache_set('my_key', $cached_data, '', 3600);
}
Additionally, Redis and Memcached improve performance significantly.
Server and Hosting Optimization
1. Choose Quality Hosting
Hosting directly impacts performance:
Recommended Hosting Types:
- Managed WordPress: WP Engine, Kinsta
- Cloud Hosting: DigitalOcean, Cloudways
- Shared Hosting: SiteGround, A2 Hosting
Moreover, premium hosting provides better performance. Therefore, invest in quality infrastructure.
2. Use HTTP/2 or HTTP/3
Modern protocols improve performance:
- First, HTTP/2 enables multiplexing
- Additionally, it reduces connection overhead
- Moreover, HTTP/3 uses QUIC protocol
- Furthermore, it handles packet loss better
- Finally, it improves mobile performance
3. Enable Server-Side Compression
Configure server compression:
# Nginx example
gzip on;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_min_length 1024;
gzip_types text/plain text/css text/xml text/javascript
application/x-javascript application/xml+rss
application/javascript application/json;
4. Optimize PHP Configuration
For PHP-based sites:
memory_limit = 256M
max_execution_time = 60
upload_max_filesize = 64M
post_max_size = 64M
opcache.enable=1
opcache.memory_consumption=128
Additionally, use latest PHP version. Moreover, PHP 8+ is significantly faster.
WordPress-Specific Optimization
1. Use Caching Plugins
Top Caching Plugins:
- WP Rocket – Premium, comprehensive
- W3 Total Cache – Free, powerful
- WP Super Cache – Simple, effective
2. Optimize WordPress Database
Database Optimization Plugins:
- WP-Optimize – Clean and compress
- Advanced Database Cleaner – Remove orphaned data
3. Limit Post Revisions
Add to wp-config.php:
define('WP_POST_REVISIONS', 3);
define('AUTOSAVE_INTERVAL', 300);
4. Disable Unnecessary Features
// Disable emoji scripts
remove_action('wp_head', 'print_emoji_detection_script', 7);
remove_action('wp_print_styles', 'print_emoji_styles');
// Disable embeds
remove_action('wp_head', 'wp_oembed_add_discovery_links');
Mobile Optimization
1. Implement Responsive Design
Use mobile-first approach:
/* Mobile first */
.container {
width: 100%;
padding: 10px;
}
/* Desktop */
@media (min-width: 768px) {
.container {
width: 750px;
padding: 15px;
}
}
2. Optimize for Touch
Ensure adequate touch targets:
button, a {
min-height: 44px;
min-width: 44px;
padding: 12px 16px;
}
3. Reduce Mobile Payload
- First, serve smaller images to mobile
- Additionally, reduce JavaScript for mobile
- Moreover, simplify mobile layouts
- Furthermore, eliminate non-essential features
- Finally, test on real devices
Advanced Optimization Techniques
1. Implement Resource Hints
Optimize resource loading:
<!-- DNS prefetch -->
<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//fonts.googleapis.com">
<!-- Preconnect -->
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.gstatic.com" crossorigin>
<!-- Prefetch -->
<link rel="prefetch" href="/next-page.html">
<!-- Preload -->
<link rel="preload" href="font.woff2" as="font" type="font/woff2" crossorigin>
2. Use Service Workers
Implement progressive web app features:
// Register service worker
if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) {
navigator.serviceWorker.register('/sw.js');
}
// Service worker caching
self.addEventListener('fetch', event => {
event.respondWith(
caches.match(event.request)
.then(response => response || fetch(event.request))
);
});
3. Implement Critical Rendering Path
Optimize rendering sequence:
- First, minimize critical resources
- Additionally, reduce critical file size
- Moreover, shorten critical path length
- Furthermore, prioritize visible content
- Finally, defer non-critical resources
4. Use Modern Loading Strategies
Implement progressive enhancement:
<!-- Priority hints -->
<img src="hero.jpg" fetchpriority="high">
<img src="footer.jpg" fetchpriority="low">
<!-- Native lazy loading -->
<img src="image.jpg" loading="lazy">
<!-- Async decoding -->
<img src="large.jpg" decoding="async">
Monitoring and Maintenance
1. Continuous Performance Monitoring
Track performance over time:
Real User Monitoring (RUM): Measure actual user experiences. Additionally, tools like Google Analytics track real performance. Moreover, RUM provides actionable insights.
Synthetic Monitoring: Regular automated tests catch regressions. Furthermore, schedule daily performance audits. Therefore, identify issues before users experience them.
2. Set Performance Budgets
Define acceptable performance thresholds:
// Performance budget example
{
"budgets": [
{
"resourceSizes": [
{"resourceType": "script", "budget": 300},
{"resourceType": "total", "budget": 1000}
]
}
]
}
3. Regular Audits
Schedule monthly performance reviews:
- First, test all critical pages
- Additionally, check mobile performance
- Moreover, audit third-party scripts
- Furthermore, update optimization strategies
- Finally, document performance trends
Common Speed Optimization Mistakes
1. Over-Optimization
Don’t sacrifice usability for speed. Moreover, balance performance with functionality. Therefore, focus on meaningful optimizations.
2. Ignoring Mobile
Over 60% of website traffic comes from mobile devices. Therefore, prioritize mobile optimization. Additionally, test on real mobile devices.
3. Not Testing Real Performance
Lab data differs from real-world performance. Moreover, test on actual devices and connections. Therefore, use field data for decisions.
4. Neglecting Content Updates
Performance degrades over time. Additionally, new content adds weight. Therefore, maintain optimization continuously.
5. Focusing Only on Tools
Don’t chase perfect scores. Moreover, prioritize actual user experience. Therefore, use tools as guides, not goals.
Website Speed Optimization Checklist
Immediate Actions (Do Today):
- ☑ Enable Gzip/Brotli compression
- ☑ Implement browser caching
- ☑ Optimize and compress images
- ☑ Minify CSS and JavaScript
- ☑ Enable lazy loading for images
Short-Term Actions (This Week):
- ☑ Set up CDN
- ☑ Implement caching plugin
- ☑ Audit and remove unused code
- ☑ Optimize database
- ☑ Test Core Web Vitals
Long-Term Actions (This Month):
- ☑ Upgrade hosting if needed
- ☑ Implement service workers
- ☑ Optimize critical rendering path
- ☑ Set up performance monitoring
- ☑ Create performance budget
Ongoing Maintenance:
- ☑ Monitor performance weekly
- ☑ Audit third-party scripts monthly
- ☑ Update optimization strategies quarterly
- ☑ Clean database regularly
- ☑ Test on real devices frequently
Frequently Asked Questions
What is website speed optimization?
Website speed optimization is the process of improving page load times and performance. Moreover, it involves technical improvements that make websites faster. Additionally, optimization enhances user experience and SEO rankings.
Why is website speed important?
Fast websites provide better user experiences and rank higher in search results. Additionally, speed directly impacts conversions and revenue. Moreover, Google uses Core Web Vitals as ranking factors. Therefore, speed optimization is essential for success.
What are Core Web Vitals?
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics that measure real-world user experience. Specifically, they include LCP, INP, and CLS. Moreover, these metrics assess loading, interactivity, and visual stability.
How can I test my website speed?
Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, and WebPageTest. Additionally, check Google Search Console for Core Web Vitals data. Moreover, test on real devices for accurate results.
What’s a good page load time?
Pages should load in under 2.5 seconds for optimal experience. Additionally, aim for under 3 seconds on mobile. Moreover, faster is always better for users and conversions.
Do images really slow down websites?
Yes, images account for approximately 50% of page weight. Moreover, unoptimized images cause slow load times. Therefore, image optimization is critical for speed.
Should I use a CDN?
Yes, CDNs significantly improve performance globally. Additionally, they reduce server load and bandwidth costs. Moreover, most CDNs offer affordable or free tiers. Therefore, CDNs benefit all websites.
How often should I optimize my website?
Perform comprehensive audits quarterly. Additionally, monitor performance weekly. Moreover, optimize new content immediately. Finally, maintain optimization continuously.
Can caching improve website speed?
Yes, caching dramatically improves performance. Additionally, it reduces server load and database queries. Moreover, properly configured caching provides instant page delivery. Therefore, caching is essential for optimization.
What’s the difference between lab and field data?
Lab data comes from controlled testing environments. Additionally, field data measures real user experiences. Moreover, both provide valuable insights. Therefore, use both for comprehensive analysis.
Conclusion
Website speed optimization is essential for success in 2025. Moreover, fast websites provide better experiences, rank higher, and convert better. Additionally, optimization is an ongoing process requiring regular attention.
Start with high-impact improvements like image optimization and caching. Furthermore, progressively implement advanced techniques. Moreover, monitor performance continuously and adjust strategies accordingly. Therefore, commit to speed optimization for long-term success.
Remember, every millisecond matters. Additionally, users expect instant experiences. Moreover, competitors are optimizing constantly. Therefore, make website speed optimization a priority today.
Additional Resources
Official Documentation
Optimization Tools
Learning Resources
Community Resources
Last Updated: December 2025 | Reading Time: 22 minutes